
- Android中ListView设置静态数据的方法
- Android编程之非调用系统界面实现发送彩信的方法(MMS)
- Android实现手写签名
- android:descendantFocusability方法介绍
- Android中判断是否有前置摄像头、后置摄像头的方法
- Android设置TextView首行缩进示例代码
- [Android开发从零开始].11.AbsoluteLayout和FrameLayout
- 基于Android实现保存图片到本地并可以在相册中显示出来
- Android编程使用内容提供者方式(ContentProvider)进行存储的方法
- Android下拉刷新官方版
- Android实现的状态栏定制和修改方法
- Android系统模拟位置的使用方法
- Android支付宝支付开发实例
- android根据分辨率自动调整字体大小的实例代码
- Android多线程处理机制中的Handler使用介绍
- android中UI主线程与子线程深入分析
- Android笔记之:onConfigurationChanged详解
- Android应用开发中CardView的初步使用指南
- 详解Android中Notification通知提醒
- Android自定义控件ViewGroup实现标签云(四)
- 解决RecycleView分割线不居中的三种方法
- Android实现沉浸式通知栏通知栏背景颜色跟随app导航栏背景颜色而改变
- Android三种方式实现ProgressBar自定义圆形进度条
- android中Bitmap的放大和缩小实例代码
- Android中通过AsyncTask类来制作炫酷进度条的实例教程
- Android编程之OpenGL绘图技巧总结
- Android中利用App实现消息推送机制的代码
- 给大家分享一些安卓自学心得
- Android开发之注册登录方法示例
- 详解Android中Handler的使用方法
Android App应用启动分析与优化
app的启动方式:
1.)冷启动
当启动应用时,后台没有该应用的进程,这时系统会重新创建一个新的进程分配给该应用,这个启动方式就是冷启动。冷启动因为系统会重新创建一个新的进程分配给它,所以会先创建和初始化Application类,再创建和初始化MainActivity类(包括一系列的测量、布局、绘制),最后显示在界面上。
2.)热启动
当启动应用时,后台已有该应用的进程(例:按back键、home键,应用虽然会退出,但是该应用的进程是依然会保留在后台,可进入任务列表查看),所以在已有进程的情况下,这种启动会从已有的进程中来启动应用,这个方式叫热启动。热启动因为会从已有的进程中来启动,所以热启动就不会走Application这步了,而是直接走MainActivity(包括一系列的测量、布局、绘制),所以热启动的过程只需要创建和初始化一个MainActivity就行了,而不必创建和初始化Application,因为一个应用从新进程的创建到进程的销毁,Application只会初始化一次。
app的启动流程:
通过上面的两种启动方式可以看出app启动流程为:
Application的构造器方法——>attachBaseContext()——>onCreate()——>Activity的构造方法——>onCreate()——>配置主题中背景等属性——>onStart()——>onResume()——>测量布局绘制显示在界面上
app的启动优化:
基于上面的启动流程我们尽量做到如下几点
1.Application的创建过程中尽量少的进行耗时操作
2.如果用到SharePreference,尽量在异步线程中操作
3.减少布局的层次,并且生命周期回调的方法中尽量减少耗时的操作
app启动遇见黑屏或者白屏问题
1.)产生原因
其实显示黑屏或者白屏实属正常,这是因为还没加载到布局文件,就已经显示了window窗口背景,黑屏白屏就是window窗口背景。
示例:
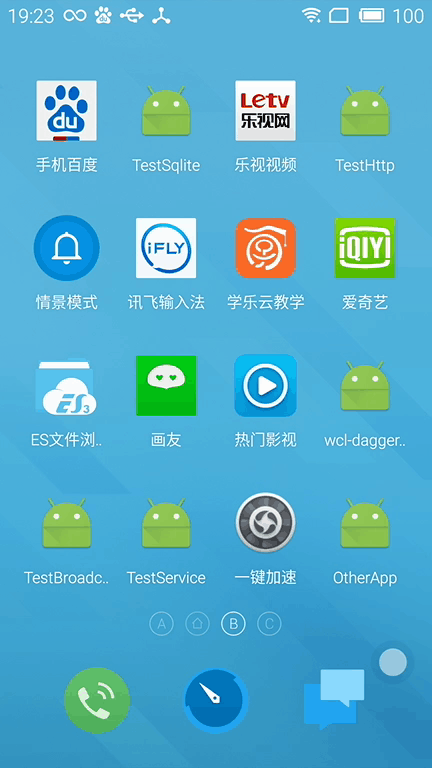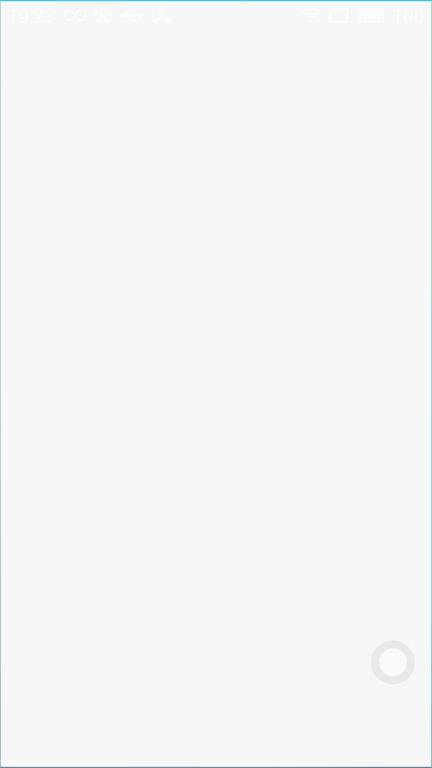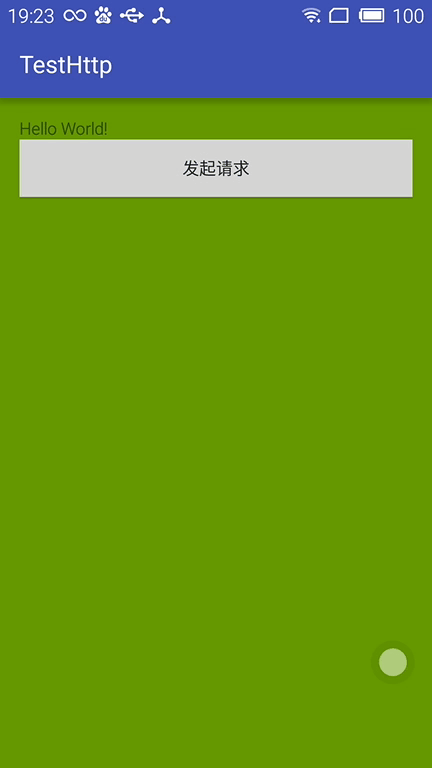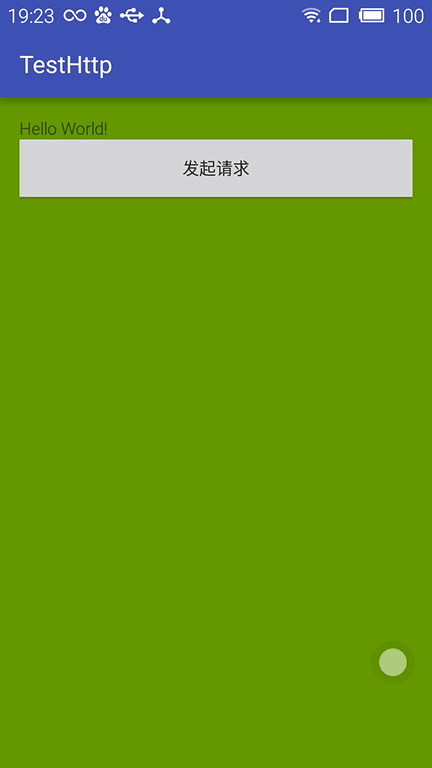
2.)解决办法
通过设置设置Style
(1)设置背景图Theme
通过设置一张背景图。 当程序启动时,首先显示这张背景图,避免出现黑屏
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="android:screenOrientation">portrait</item>
<item name="android:windowBackground">>@mipmap/splash</item>
<item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item>
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
</style>
(2)设置透明Theme
通过把样式设置为透明,程序启动后不会黑屏而是整个透明了,等到界面初始化完才一次性显示出来
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
<item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/transparent</item>
<item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item>
<item name="android:screenOrientation">portrait</item>
</style>
两者对比:
Theme1 程序启动快,界面先显示背景图,然后再刷新其他界面控件。给人刷新不同步感觉。
Theme2 给人程序启动慢感觉,界面一次性刷出来,刷新同步。
(3)修改AndroidManifest.xml
<application
android:name=".App"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
//......
</application>
解决后示例:
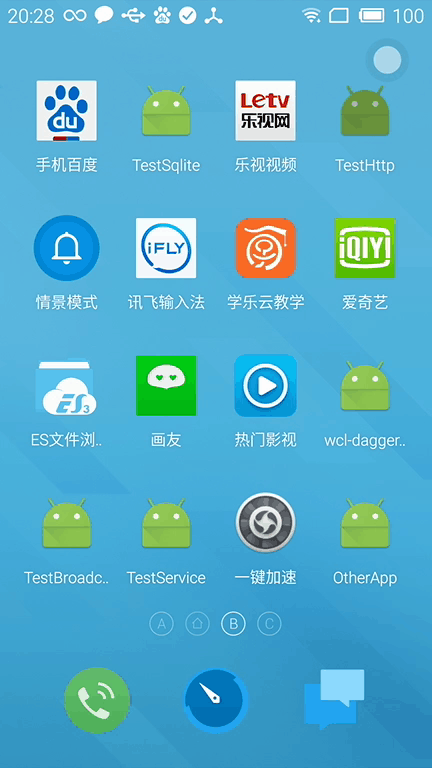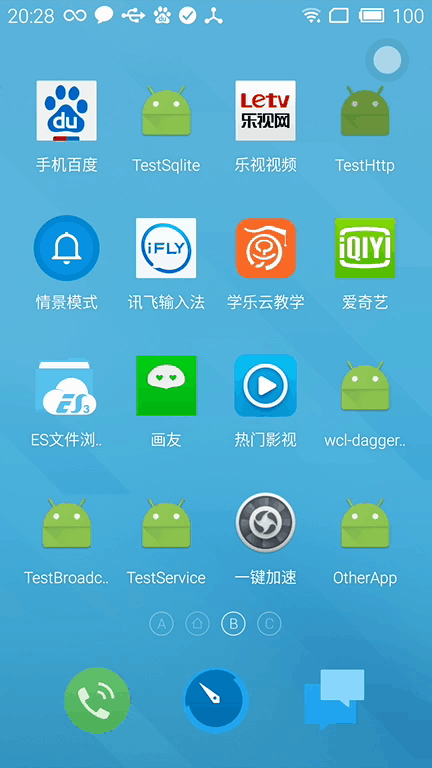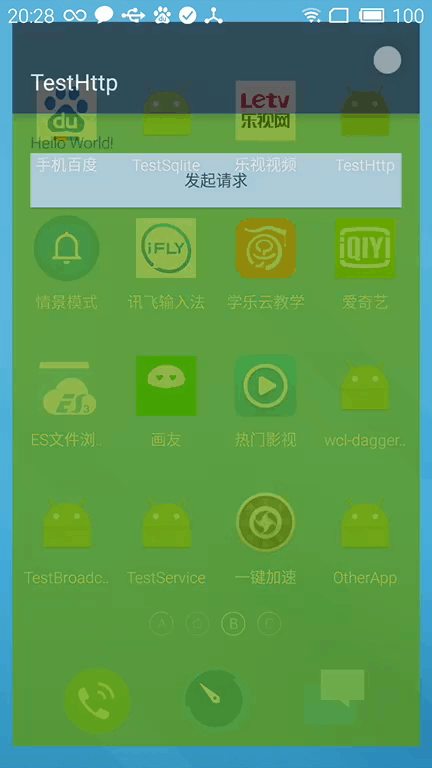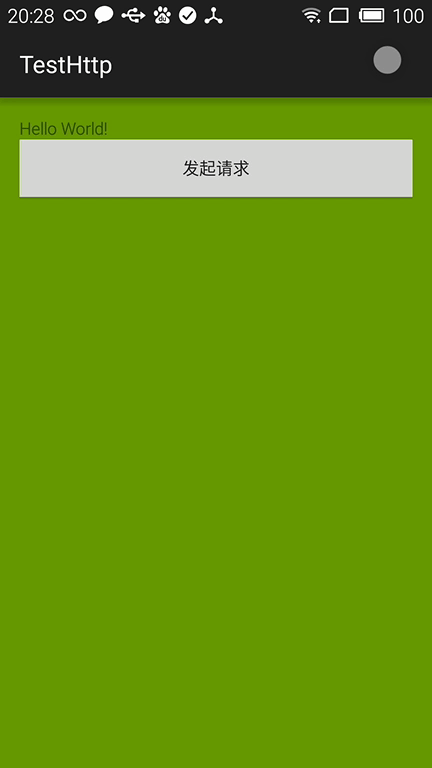
3.)常见的Theme主题
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Dialog" //Activity显示为对话框模式
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar" //不显示应用程序标题栏
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" //不显示应用程序标题栏,并全屏
android:theme="Theme.Light " //背景为白色
android:theme="Theme.Light.NoTitleBar" //白色背景并无标题栏
android:theme="Theme.Light.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" //白色背景,无标题栏,全屏
android:theme="Theme.Black" //背景黑色
android:theme="Theme.Black.NoTitleBar" //黑色背景并无标题栏
android:theme="Theme.Black.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" //黑色背景,无标题栏,全屏
android:theme="Theme.Wallpaper" //用系统桌面为应用程序背景
android:theme="Theme.Wallpaper.NoTitleBar" //用系统桌面为应用程序背景,且无标题栏
android:theme="Theme.Wallpaper.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" //用系统桌面为应用程序背景,无标题栏,全屏
android:theme="Theme.Translucent" //透明背景
android:theme="Theme.Translucent.NoTitleBar" //透明背景并无标题
android:theme="Theme.Translucent.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" //透明背景并无标题,全屏
android:theme="Theme.Panel " //面板风格显示
android:theme="Theme.Light.Panel" //平板风格显示
干我们这行,啥时候懈怠,就意味着长进的停止,长进的停止就意味着被淘汰,只能往前冲,直到凤凰涅槃的一天!
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
- 上一篇文章: 解决Android MediaRecorder录制视频过短问题
- 下一篇文章: 超酷炫的Android碎纸机效果推荐
- 实例详解用户输入 i. 检测常用手势
- Android通讯录开发之删除功能的实现方法
- [Android开发从零开始].23.数据存储(2)
- Android应用开发中模拟按下HOME键的效果(实
- 解析:ClickOnce通过URL传递参数 XXX.applic
- android检查手机和无线是否连接的方法
- Android日期时间格式国际化的实现代码