
- iOS开发之手势识别
- ios播放声音中断后台音乐的问题
- iOS开发中使用Picker View实现一个点菜应用的UI示例
- 详解iOS应用程序的启动过程
- 【iOS】被忽略的main函数
- objective-c语法快速过(3)
- 关于堆栈
- iOS App开发中使cell高度自适应的黑魔法详解
- AppStore企业账号打包发布APP流程详解
- [转]AsyncDisplayKit教程:达到60FPS的滚动帧率
- 数据库使用之第三方库FMDB
- IOS04汤姆猫开发
- IOS开发的一些小技巧
- Swift闭包表达式
- FIR.imWeekly-技术是练出来的
- IOS开发之自定义Button(集成三种回调模式)
- IOS学习笔记----15/09/01
- 实例讲解iOS应用的设计模式开发中的Visitor访问者模式
- IOS基本数据类型之枚举
- 沙盒目录常用获取方式
- copy和mutableCopy的深、浅拷贝
- swift动画小试牛刀
- Swift的基本类型和流程控制
- (转)iOS中的唯一标示符
- 在IOS中为什么使用多线程及多线程实现的三种方法
- [oc学习日记]kvc,kvo和通知
- Quartz-2D绘图之路径(Paths)详解
- iOS开发中一些手写控件及其相关属性的使用
- Category
- IOSApplication新建Empty项目中自定义UIButton
iOS开发中使用SQL语句操作数据库的基本用法指南
SQL代码应用示例
一、使用代码的方式批量添加(导入)数据到数据库中
1.执行SQL语句在数据库中添加一条信息

插入一条数据的sql语句:

点击run执行语句之后,刷新数据

2.在ios项目中使用代码批量添加多行数据示例
代码示例:
复制代码 代码如下:
//
// main.m
// 01-为数据库添加多行数据
//
// Created by apple on 14-7-26.
// Copyright (c) 2014年 wendingding. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
NSArray *names=@[@"张一",@"张二",@"张三",@"张四"];
NSMutableString *sql=[NSMutableString string];
for (int i=0; i<200; i++) {
int ID=i+1;
//这里的警告为无符号类型转换
NSString *name=names[arc4random_uniform(names.count)];
name=[name stringByAppendingFormat:@"-%d",arc4random_uniform(200)];
//生成随机数,范围以20为中心上下波动10
int age=arc4random_uniform(20)+10;
[sql appendFormat:@"INSERT INTO t_student (id,name,age) VALUES (%d,'%@',%d);\n",ID,name,age];
}
//把sql写入到文件中
[sql writeToFile:@"/Users/apple/Desk/students.sql" atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSLog(@"\n%@",sql);
}
return 0;
}
作用:生成200条相应的sql插入语句
打印结果为:

使用文本编辑器,打开生成的sql文件。

可以把这些SQL语句拷贝到Navicat中进行执行,也可以直接执行整个文件。
在数据库中创建一张表:

选择执行SQL文件:

执行完毕后,点击cancel。

刷新数据库,查看插入的200条数据

二、分页简单演示
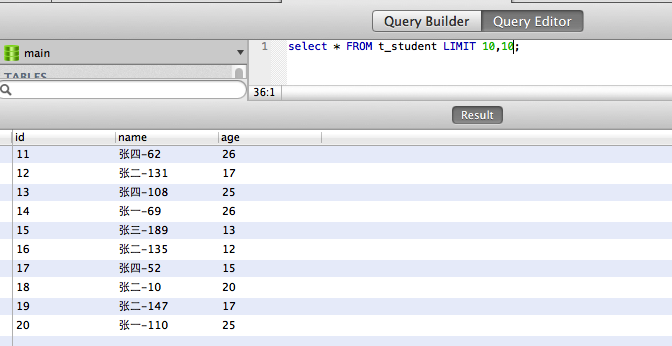
说明:
使用limit可以精确地控制查询结果的数量,比如每次只查询10条数据
格式 select * from 表名 limit 数值1, 数值2 ;
示例
select * from t_student limit 4, 8 ;
可以理解为:跳过最前面4条语句,然后取8条记录
limit常用来做分页查询,比如每页固定显示5条数据,那么应该这样取数据
第1页:limit 0, 5
第2页:limit 5, 5
第3页:limit 10, 5
…
第n页:limit 5*(n-1), 5
下面语句的作用
select * from t_student limit 7 ;
相当于select * from t_student limit 0, 7 ;表示取最前面的7条记录
三、补充
1.关于外键约束(建立起两张表之间的联系)
第一种做法:可以新建一张关系表,让之前两张表(班级表和学生表建立起对应的联系),但是这种做法很冗余,没有必要
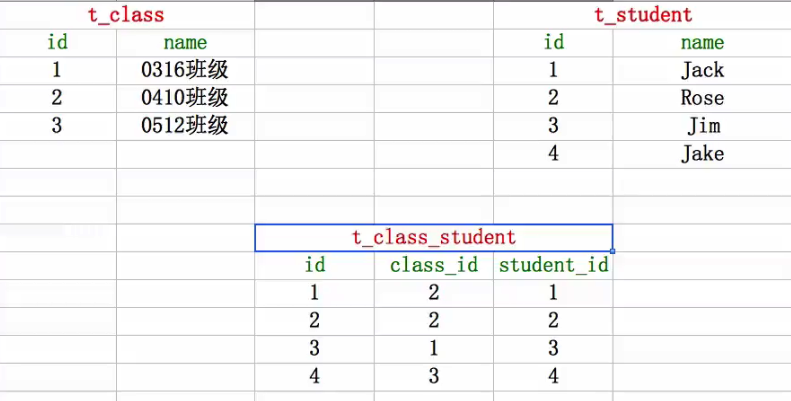
第二种做法:使用外键约束
一对一,一对多,多对多关系。当两张表有联系时,如何设置外键(在哪张表中设置?)

2.关于表连接
子查询:要求查询所有类型为粤菜的菜名。

查询结果为:

连接查询:
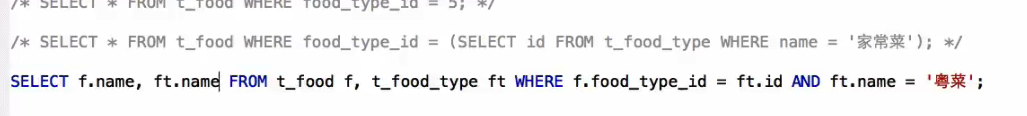
查询结果为:

PS:常用的SQL语句整理
一、SQL语句
如果要在程序运行过程中操作数据库中的数据,那得先学会使用SQL语句
1.什么是SQL
SQL(structured query language):结构化查询语言
SQL是一种对关系型数据库中的数据进行定义和操作的语言
SQL语言简洁,语法简单,好学好用
2.什么是SQL语句
使用SQL语言编写出来的句子\代码,就是SQL语句
在程序运行过程中,要想操作(增删改查,CRUD)数据库中的数据,必须使用SQL语句
3.SQL语句的特点
不区分大小写(比如数据库认为user和UsEr是一样的)
每条语句都必须以分号 ; 结尾
4.SQL中的常用关键字有
select、insert、update、delete、from、create、where、desc、order、by、group、table、alter、view、index等等
数据库中不可以使用关键字来命名表、字段
二、SQL语句的种类
1.数据定义语句(DDL:Data Definition Language)
包括create和drop等操作
在数据库中创建新表或删除表(create table或 drop table)
2.数据操作语句(DML:Data Manipulation Language)
包括insert、update、delete等操作
上面的3种操作分别用于添加、修改、删除表中的数据
3.数据查询语句(DQL:Data Query Language)
可以用于查询获得表中的数据
关键字select是DQL(也是所有SQL)用得最多的操作
其他DQL常用的关键字有where,order by,group by和having
三、基本操作
1.创建表
create table 表名 (字段名1 字段类型1, 字段名2 字段类型2, …) ;
create table if not exists 表名 (字段名1 字段类型1, 字段名2 字段类型2, …) ;
示例
create table t_student (id integer, name text, age integer, score real) ;
2.字段类型
SQLite将数据划分为以下几种存储类型:
integer : 整型值
real : 浮点值
text : 文本字符串
blob : 二进制数据(比如文件)
注意:实际上SQLite是无类型的,就算声明为integer类型,还是能存储字符串文本(主键除外)
建表时声明啥类型或者不声明类型都可以,也就意味着创表语句可以这么写:
create table t_student(name, age);
提示:为了保持良好的编程规范、方便程序员之间的交流,编写建表语句的时候最好加上每个字段的具体类型
3.删表
格式
drop table 表名 ;
drop table if exists 表名 ;
示例
drop table t_student ;
4.插入数据(insert)
格式
insert into 表名 (字段1, 字段2, …) values (字段1的值, 字段2的值, …) ;
示例
insert into t_student (name, age) values (‘mj', 10) ;
注意
数据库中的字符串内容应该用单引号 ' 括住
5.更新数据(update)
格式
update 表名 set 字段1 = 字段1的值, 字段2 = 字段2的值, … ;
示例
update t_student set name = ‘jack', age = 20 ;
注意
上面的示例会将t_student表中所有记录的name都改为jack,age都改为20
6.删除数据(delete)
格式
delete from 表名 ;
示例
delete from t_student ;
注意
上面的示例会将t_student表中所有记录都删掉
7.条件语句
如果只想更新或者删除某些固定的记录,那就必须在DML语句后加上一些条件
条件语句的常见格式
where 字段 = 某个值 ; // 不能用两个 =
where 字段 is 某个值 ; // is 相当于 =
where 字段 != 某个值 ;
where 字段 is not 某个值 ; // is not 相当于 !=
where 字段 > 某个值 ;
where 字段1 = 某个值 and 字段2 > 某个值 ; // and相当于C语言中的 &&
where 字段1 = 某个值 or 字段2 = 某个值 ; // or 相当于C语言中的 ||
示例
将t_student表中年龄大于10 并且 姓名不等于jack的记录,年龄都改为 5
update t_student set age = 5 where age > 10 and name != ‘jack' ;
删除t_student表中年龄小于等于10 或者 年龄大于30的记录
delete from t_student where age <= 10 or age > 30 ;
猜猜下面语句的作用
update t_student set score = age where name = ‘jack' ;
将t_student表中名字等于jack的记录,score字段的值 都改为 age字段的值
8.DQL语句
格式
select 字段1, 字段2, … from 表名 ; select * from 表名; // 查询所有的字段
示例
select name, age from t_student ; select * from t_student ; select * from t_student where age > 10 ; // 条件查询
9.起别名
格式(字段和表都可以起别名)
select 字段1 别名 , 字段2 别名 , … from 表名 别名 ;
select 字段1 别名, 字段2 as 别名, … from 表名 as 别名 ;
select 别名.字段1, 别名.字段2, … from 表名 别名 ;
示例
select name myname, age myage from t_student ;
给name起个叫做myname的别名,给age起个叫做myage的别名
select s.name, s.age from t_student s ;
给t_student表起个别名叫做s,利用s来引用表中的字段
10.计算记录的数量
格式
select count (字段) from 表名 ;
select count ( * ) from 表名 ;
示例
select count (age) from t_student ; select count ( * ) from t_student where score >= 60;
11.排序
查询出来的结果可以用order by进行排序
select * from t_student order by 字段 ;
select * from t_student order by age ;
默认是按照升序排序(由小到大),也可以变为降序(由大到小)
select * from t_student order by age desc ; //降序 select * from t_student order by age asc ; // 升序(默认)
也可以用多个字段进行排序
select * from t_student order by age asc, height desc ;
先按照年龄排序(升序),年龄相等就按照身高排序(降序)
12.limit
使用limit可以精确地控制查询结果的数量,比如每次只查询10条数据
格式
select * from 表名 limit 数值1, 数值2 ;
示例
select * from t_student limit 4, 8 ;
可以理解为:跳过最前面4条语句,然后取8条记录
limit常用来做分页查询,比如每页固定显示5条数据,那么应该这样取数据
第1页:limit 0, 5
第2页:limit 5, 5
第3页:limit 10, 5
…
第n页:limit 5*(n-1), 5
select * from t_student limit 7 ;这条语句的作用相当于select * from t_student limit 0, 7 ;表示取最前面的7条记录
四、约束
1.简单约束
建表时可以给特定的字段设置一些约束条件,常见的约束有
not null :规定字段的值不能为null
unique :规定字段的值必须唯一
default :指定字段的默认值
(建议:尽量给字段设定严格的约束,以保证数据的规范性)
示例
create table t_student (id integer, name text not null unique, age integer not null default 1) ;
name字段不能为null,并且唯一
age字段不能为null,并且默认为1
2.主键约束
(1)简单说明
如果t_student表中就name和age两个字段,而且有些记录的name和age字段的值都一样时,那么就没法区分这些数据,造成数据库的记录不唯一,这样就不方便管理数据
良好的数据库编程规范应该要保证每条记录的唯一性,为此,增加了主键约束
也就是说,每张表都必须有一个主键,用来标识记录的唯一性
(2)什么是主键?
主键(Primary Key,简称PK)用来唯一地标识某一条记录
例如t_student可以增加一个id字段作为主键,相当于人的身份证
主键可以是一个字段或多个字段
(3)主键的设计原则
主键应当是对用户没有意义的
永远也不要更新主键
主键不应包含动态变化的数据
主键应当由计算机自动生成
(4)主键的声明
在创表的时候用primary key声明一个主键
create table t_student (id integer primary key, name text, age integer) ;
integer类型的id作为t_student表的主键
主键字段
只要声明为primary key,就说明是一个主键字段
主键字段默认就包含了not null 和 unique 两个约束
说明:如果想要让主键自动增长(必须是integer类型),应该增加autoincrement
create table t_student (id integer primary key autoincrement, name text, age integer) ;
3.外键约束
利用外键约束可以用来建立表与表之间的联系
外键的一般情况是:一张表的某个字段,引用着另一张表的主键字段
新建一个外键
create table t_student (id integer primary key autoincrement, name text, age integer, class_id integer, constraint fk_student_class foreign key (class_id) references t_class (id));
t_student表中有一个叫做fk_t_student_class_id_t_class_id的外键
这个外键的作用是用t_student表中的class_id字段引用t_class表的id字段
4.表连接查询
表连接查询:需要联合多张表才能查到想要的数据
表连接的类型
内连接:inner join 或者 join (显示的是左右表都有完整字段值的记录)
左外连接:left outer join (保证左表数据的完整性)
示例
查询0316iOS班的所有学生
select s.name,s.age from t_student s, t_class c where s.class_id = c.id and c.name = ‘0316iOS';