·您现在的位置: 云翼网络 >> 文章中心 >> 网站建设 >> 网站建设开发 >> ASP.NET网站开发 >> 如何实现SQL事务的提交,又不对外进行污染(2)
- 关闭按钮点击事件的捕捉
- ASP.NET - TreeView Web 服务器控件事件
- solr与.net系列课程(五)solrnet的使用
- FileUpload无法赋值解决方案
- 手把手教你建立ASP.NET开发平台
- .Net2.0读取应用程序配置节
- 上传功能
- asp.net发邮件功能
- 如何在客户端清除fileUpLoad控件的文件路径
- 在ASP.NET中实现多文件上传
- 在Asp.net用C#建立动态Excel(外文翻译)
- OutputCache属性详解(三)— VaryByHeader,VaryByCustom
- ASP.NET 2.0快速入门(6):ASP.NET 2.0 成员管理
- DATATable转为json
- 一个极有可能引发ExecutionEngineException的情况
- ASP.NET页面模型
- ASP.NET 数据绑定函数Eval()的机制
- ASP.NET 在 Windows Azure 环境中使用基于 SQLServer 的 Session
- 数字的转换char to int(Convert.ToInt32() & int.Parse())
- .NET开源工作流RoadFlow-表单设计-新建表单(属性设置)
- C#内存管理优化实践
- ASP.Net 验证视图状态 MAC 失败
- ASP.NET中备份SQL Server数据库的方法
- 编程面试中的十个常见错误
- 将SQL SERVER数据库改成MySql
- ASP.NET MVC5利用EF,反向自动生成数据库
- 【ASP.NET基础】表单和控件
- Winform上传下载文件代码
- Cheatsheet:201506.01~06.30
- .Net实现IO操作
如何实现SQL事务的提交,又不对外进行污染(2)
作者:佚名 ASP.NET网站开发编辑:admin 更新时间:2022-07-23
如何实现SQL事务的提交,又不对外进行污染(2)
紧接着上文,这里主要记录事务操作,实现多实体的功能
在SqlTran类中添加方法如下:
1、两个不同实体类型的事务方法:
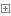
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 执行事务(事务中不同实体) 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <typeparam name="T">实体</typeparam> 5 /// <param name="method">要执行的方法(SqlTransaction 默认传入为null)</param> 6 /// <param name="obj1">参数值</param> 7 /// <returns></returns> 8 public static Int32 ExecuteTran<M, N>(Func<M, SqlTransaction, Int32> method1, Func<N, SqlTransaction, Int32> method2, M obj1, N obj2) 9 where M : new()10 where N : new()11 {12 Int32 count = 0;13 SqlConnection conn = null;14 SqlTransaction tran = null;15 try16 {17 conn = new SqlConnection(Repository.connStr);18 conn.Open();19 tran = conn.BeginTransaction();20 21 count += method1(obj1, tran);22 count += method2(obj2, tran);23 24 tran.Commit();25 return count;26 }27 catch (Exception ex)28 {29 tran.Rollback();30 return -1;31 }32 finally33 {34 if (tran != null)35 tran.Dispose();36 if (conn != null)37 {38 conn.Close();39 conn.Dispose();40 }41 }42 43 }44 45 /// <summary>46 /// 执行事务(事务中不同实体)47 /// </summary>48 /// <typeparam name="T">实体</typeparam>49 /// <param name="method">要执行的方法(SqlTransaction 默认传入为null)</param>50 /// <param name="obj1">参数值</param>51 /// <returns></returns>52 public static Int32 ExecuteTran<M, N>(IList<Func<M, SqlTransaction, Int32>> methods1, IList<Func<N, SqlTransaction, Int32>> methods2, IList<M> objs1, List<N> objs2)53 where M : new()54 where N : new()55 {56 Int32 count = 0;57 SqlConnection conn = null;58 SqlTransaction tran = null;59 try60 {61 conn = new SqlConnection(Repository.connStr);62 conn.Open();63 tran = conn.BeginTransaction();64 65 if (methods1.Count() != objs1.Count())66 return -1;67 if (methods2.Count() != objs2.Count())68 return -1;69 70 for (int i = 0; i < objs1.Count(); i++)71 count += methods1[i](objs1[i], tran);72 for (int i = 0; i < objs2.Count(); i++)73 count += methods2[i](objs2[i], tran);74 75 tran.Commit();76 return count;77 }78 catch (Exception ex)79 {80 tran.Rollback();81 return -1;82 }83 finally84 {85 if (tran != null)86 tran.Dispose();87 if (conn != null)88 {89 conn.Close();90 conn.Dispose();91 }92 }93 94 }View Code参数为List的时候,注意对应关系
methods1-->objs1
methods2-->objs2
2、测试方法:

1 public void Test() 2 { 3 Repository repository = new Repository(); 4 5 Orders order11 = new Orders() { Id = 11, Name = "name11" }; 6 Orders order21 = new Orders() { Id = 12, Name = "name12" }; 7 Orders order31 = new Orders() { Id = 13, Name = "name13" }; 8 OrderDetail orderDetail11 = new OrderDetail() { Id = 11, OrderId = 1, Name = "namedetail11" }; 9 OrderDetail orderDetail12 = new OrderDetail() { Id = 12, OrderId = 1, Name = "namedetail12" };10 11 var count1 = SqlTran.ExecuteTran<Orders, OrderDetail>(repository.AddOrder, repository.AddOrderDetail, order11, orderDetail11); //不同方法,不同实体类型12 13 List<Func<Orders, SqlTransaction, Int32>> listFuncOrders = new List<Func<Orders, SqlTransaction, Int32>>();14 List<Func<OrderDetail, SqlTransaction, Int32>> listFuncOrdersDetail = new List<Func<OrderDetail, SqlTransaction, Int32>>();15 List<Orders> listOrder = new List<Orders>();16 List<OrderDetail> listOrderDatail = new List<OrderDetail>();17 18 listFuncOrders.Add(repository.AddOrder);19 listFuncOrders.Add(repository.AddOrder);20 listOrder.Add(order21);21 listOrder.Add(order31);22 23 listFuncOrdersDetail.Add(repository.AddOrderDetail);24 listFuncOrdersDetail.Add(repository.UpdateOrderDetail);25 listOrderDatail.Add(orderDetail12);26 orderDetail11.Name = "namedetail11Update";27 listOrderDatail.Add(orderDetail11);28 29 var count2 = SqlTran.ExecuteTran<Orders, OrderDetail>(listFuncOrders, listFuncOrdersDetail, listOrder, listOrderDatail);30 }View Code3、三个不同实体类型的事务方法:定义
public static Int32 ExecuteTran<M, N, T>(Func<M, SqlTransaction, Int32> method1, Func<N, SqlTransaction, Int32> method2, Func<T, SqlTransaction, Int32> method3, M obj1, N obj2, T obj3) where M : new() where N : new() where T : new()
所以根据实体的个数进行定义就ok,之后就可以重用了
缺点之一:每个事务方法中大部分的代码是一样的,只有委托执行方法部分有微小的变化(如:count += method(obj1, tran); ),本人目前没有更好的办法把这块相同的代码提取出来进行共用,希望看到这里的同行,如果有好的解决方案,希望能拿出来互相交流!指点迷津。
- 上一篇文章: asp.net中Repeart选中整行操作
- 下一篇文章: Http 请求处理流程